AR & VR, multiplayer worlds, web 3.0: Metaverse already exists

Did you know that the Metaverse also has a middle name, at least 90% of its meaning?
No? Well, we will reveal it to you now: we are talking about cyberspace, or a network of virtual and interconnected worlds, in short, the Internet generation we are already beginning to live with.
What is being aimed at is a true democratization of the Web and everything that has hitherto been connected to it. Indeed, we are preparing for a new way of surfing, in which anyone who wants to build any space in which to essentially relate people, places and things will be able to do so.
This, thanks to the convergence of multiple technologies, which we list below.
AN EXTENDED REALITY (XR): AR and VR
One of the ways in which the user today carves out a space within three-dimensional worlds is through virtual and/or augmented reality, technologies grouped under XR (extended reality). Thanks to specific hardware such as professional glasses, viewers and headsets, we can really talk about the interrelationship between the physical and digital worlds.
But to understand this, let's give a brief definition of the technologies.
When we talk about augmented reality (AR) we refer to an "augmented" version of reality, created through the use of technology, that adds digital information by superimposing it on the real environment. To do this, augmented reality relies on the use of a smartphone (or tablet), on which an AR application can be downloaded (many are available on the iOS and Android stores, such as Ikea's app), or more sophisticated systems, such as Google Glasses.
Instead, when we talk about virtual reality (VR) we mean a technology capable of transporting us into a reality other than the one we are experiencing. This is done through visors that, when worn, are capable of isolating us from the world and teleporting us elsewhere.
Mixed reality is thus the union of these two technologies: the ability to mix (precisely) physical and digital worlds, interacting with digital elements in the physical world or moving into an entirely three-dimensional world.
This is through the use of specific visors, such as the Meta Quest Pro presented at the last Meta Connect.
Obviously, to get to a smooth interrelationship between the physical and digital worlds there is still some way ahead, but what is certain is that equipment prices have fallen, and in a very short time avatars (i.e., our 3D representations within virtual worlds) will be 100% lifelike: they will faithfully reproduce body movements, facial expressions (even projected by the user himself), and even social interactions.
In any case, what is lacking to date is filled by mobile AR technology, which uses cameras to process and superimpose the necessary information, now found on more than 6 billion smart-phones and used by 800 million people (think of Instagram filters, for example).
They say it will reach 1.7 billion by 2025. That's a lot.
A PERFECT NUMBER, 3.0: FROM WEB 2.0 TO A DEMOCRATIC WEB
What is the difference between Web 2.0 or 3.0? Taking a step back, in the initial iteration of the Internet (Web 1.0), users read or consumed digital content created by others.
With the advent of Web 2.0, users were able to both create and consume content, but centralized networks continued to control the distribution of the same content (think Google, Meta, Apple, Amazon for example).
In Web 3.0 there is a further step forward: users consume, create but most importantly own content; this means that networks (and the money exchanged, in the form of crypto) become decentralized, thanks to blockchain technology, which replaces centralized intermediaries and provides the trust that enables consumption.
This new type of economy is called democratic-a complex but not complicated concept that has been in the works for some time. Although it is only in its infancy, there are about 30 million NFT wallets, including 1 million active wallets, which spent about $40 billion on NFT purchases in 2021.
If you want to explore this further, check out this video:
A TOTAL IMMERSION: MULTIPLAYER WORLDS
Multiplayer worlds, also called M-worlds, are virtual worlds that offer brands the opportunity to reach new audiences (in particular, Gen Z) via smartphones, tablets, PC browsers, and AR or VR headsets.
Each M-world (think for example of Nikeland on Roblox) is built to host its own virtual communities and content, with its own business model and rules, and its own monetization models (subscriptions, in-app purchases, advertising, but also new tools that the metaverse will offer).
But where do these multiplayer worlds come from? Once again gaming centers: many games have become true virtual worlds by integrating features and attractions to engage the user, such as Fortnite (2017), which has progressively incorporated virtual concerts and map-making tools.
With new applications already being built, such as Meta's Horizon Worlds, Nvidia's Omniverse, and Microsoft's Mesh (which will integrate with popular Microsoft software, such as Teams), multiplayer worlds will be increasingly developed, engaging, and accessible. Why are we confident of their near success? Because of 6 of their features:
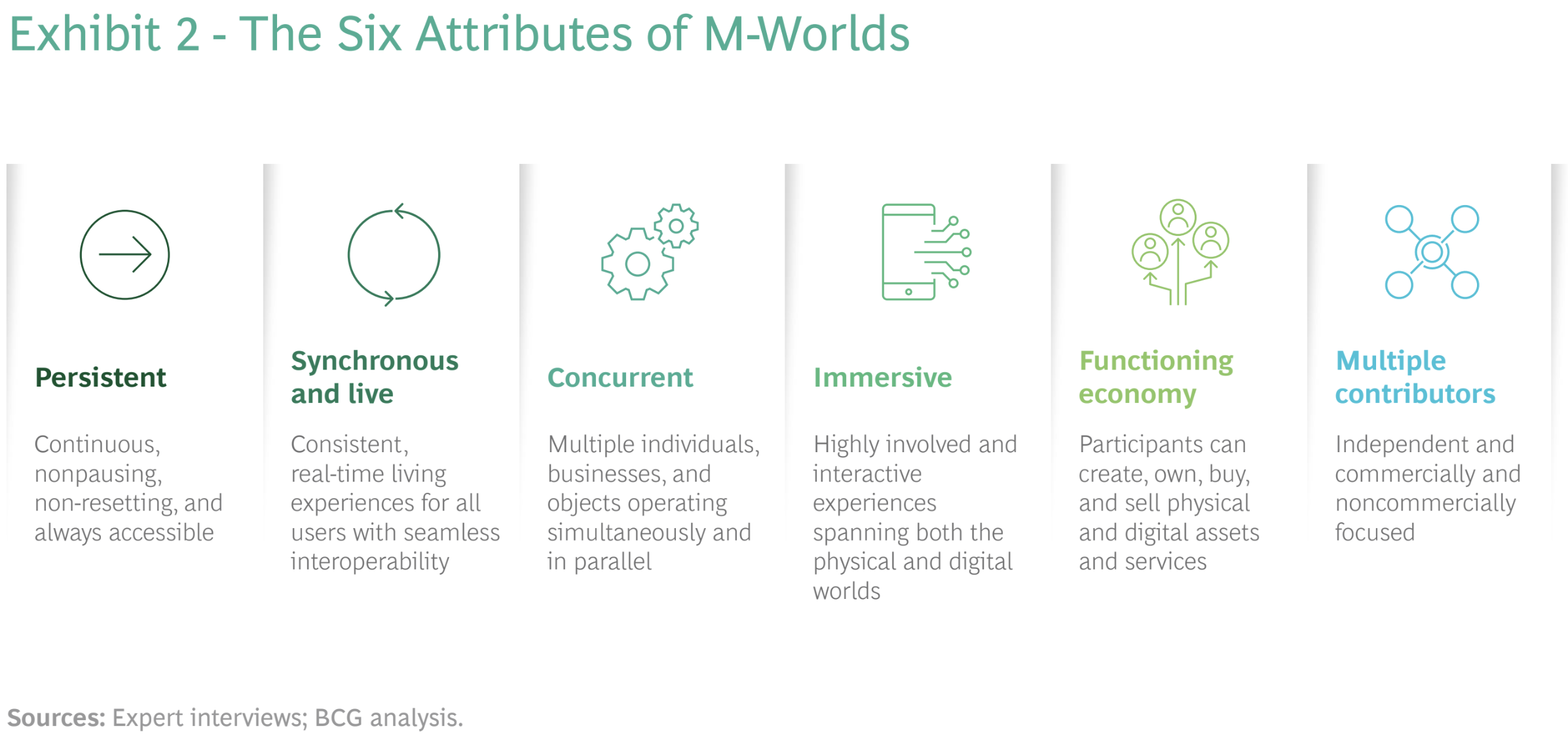
WHY SHOULD A COMPANY INVEST IN THESE TECHNOLOGIES?
Simple: because this convergence of technologies will be increasingly useful to their consumers. It will allow them to make purchases (physical and virtual) in new, immediate and personalized ways.
The same consumers will also be able to participate in exclusive experiences such as concerts and events organized by the brand, where they will be able to meet entire communities with the same interests as them and become even more attached to a lifestyle and mood conveyed by the company not only through social but through a real new world.
In a nutshell, because it is not only the customer who will come first, but also their experience with the brand. To elaborate further, we refer you to this article on how to build a marketing strategy for the metaverse.
APPROACHING SOMETHING YOU DON'T KNOW: EXPERIMENTING
All good, but where do you start, then? Moving into the virtual world without first getting to know it is a bit risky, if not useless. That's why companies should start experimenting and familiarizing themselves with the metaverse in a few simple ways:
- Buy visors and organize demonstration sessions, through teams of experts or enthusiasts and regular meetings with each other, drawing data and case studies from them.
- Invest in prototypes and new hardware
- Hire new talent, including those with interest and experience in XR and the metaverse.
- Make interest public: communicate externally that the metaverse is no longer a stranger to the brand by sharing what is being done.
- Building partnerships: the metaverse will be an ecosystem; starting to build connections now has long-term value.
Drawing conclusions, the Metaverse is not all new, it follows that not everything will be scary for a brand or its buyer. It is not easy to define, but it is also not difficult to understand what already exists.
Here we have given you an overview of what is already converging, and what is in development, but we are available for further discussion.
